Importance of Newborn, Baby, Child Vaccinations – Chart and Types

What is Newborn, Baby, Child vaccination?
Newborn, Baby or Infant, Toddler and Children are exposed to an open environment, and since their immune systems are not fully developed, they are prone to contracting a pathogen which may stir a disease in them. Unless completely treated, these diseases could prove fatal.
To void any such mishaps, the newborn, baby or infant, child can be vaccinated.
A vaccine is a dead or attenuated form of the pathogen (germ) responsible for any disease. When the child is provided with some form of vaccination, their immune system (the body's germ-fighting mechanism) can produce antibodies that protect them against catching the disease if and when exposed to the condition.
Types of vaccines
Various types of vaccines are designed to equip the immune system with the necessary means to defend the body against various germs and the fatal diseases they cause.
- Inactivated vaccines – These vaccines utilise the killed version of the germs which cause diseases. They fail to provide immunity which is as strong as live vaccines.
- Live-attenuated vaccines - These vaccines inject an attenuated form (a weakened form) of the microbe that causes a disease. They create a long-lasting immune response.
- Messenger RNA vaccines—also called mRNA vaccines – These vaccines utilise mRNA to create proteins which can trigger an immune reaction.
- Subunit, recombinant, polysaccharide, and conjugate vaccines – These vaccines utilise particular parts of the microbe, such as sugar or capsid, which provide a robust immune response.
- Toxoid vaccines – Microbes create toxins (harmful products). These vaccines utilise toxins to create immunity instead of the whole germ.
- Viral vector vaccines – A modified version of a different virus is used to deliver protection in these types of vaccines.
Why vaccination is necessary for baby, newborn or child?
Vaccinations not only keep newborn, baby or infant, children safe by eliminating or significantly reducing harmful diseases that are used to transmit from child to child, but they also protect from potentially fatal diseases such as and not limited to tetanus (lockjaw), diphtheria, hepatitis, measles, polio, tuberculosis etc.
India has the greatest number of deaths among children under the age of five years (early childhood) globally, the majority of which are due to vaccine-preventable diseases. Protection against communicable diseases requires timely vaccination to develop immunity and minimise susceptibility to infection.
Delays in vaccines beyond the recommended time frame (i.e., untimely vaccination) could expose the newborn, baby or infant, child to a prolonged risk of disease and contribute to the ongoing transmission of diseases. Therefore, vaccination timeliness is an important criterion for evaluating immunisation program performance, since coverage estimates alone may lead to incorrect assumptions about herd immunity and transmission risk.
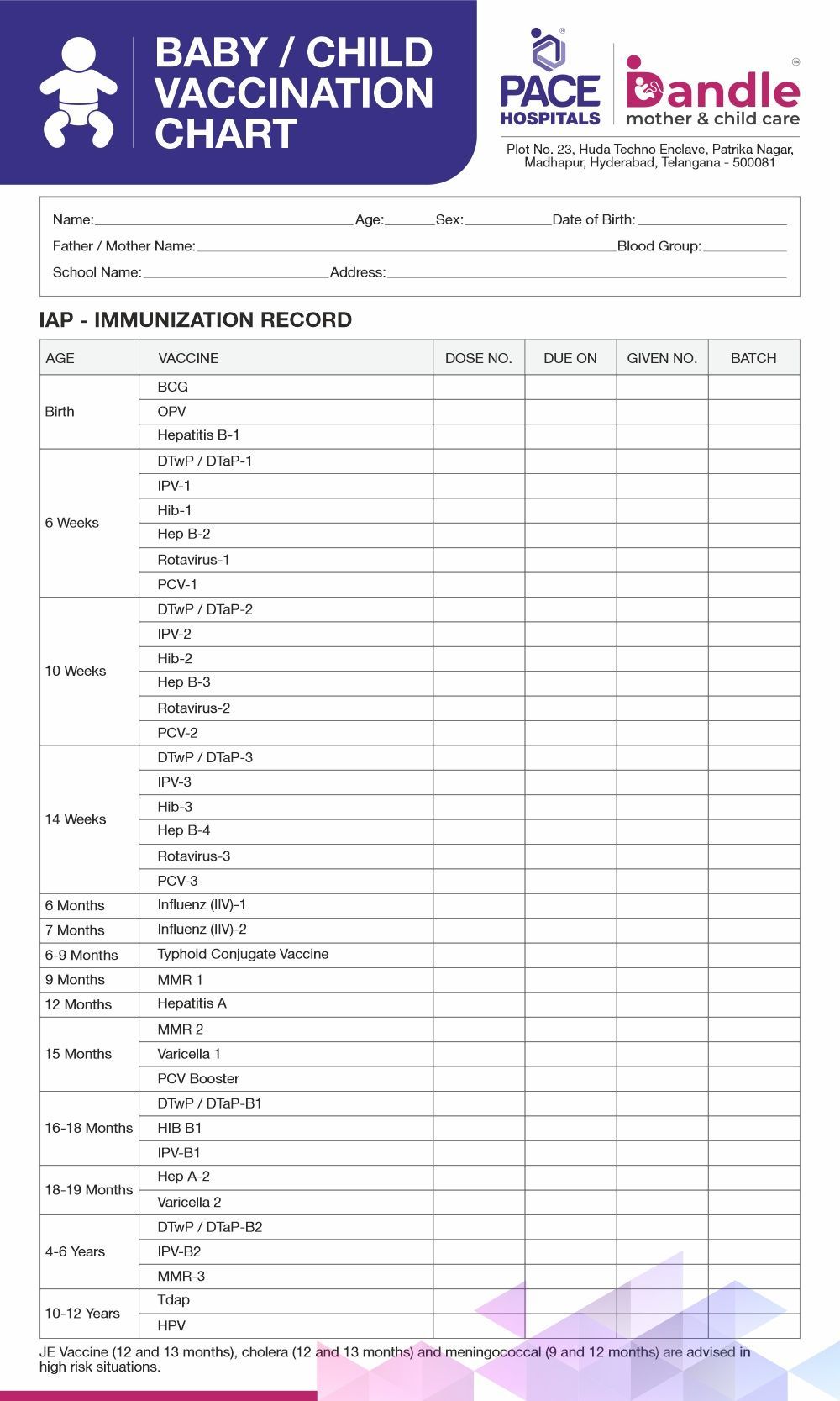
List of vaccines for babies in India | Types of vaccination
The common vaccinations which are to be done in new-borns and babies and under 1 year are as follows.
- BCG - Bacillus Calmette Guerin. This vaccine offers protection against tuberculosis.
- OPV - Oral Polio Vaccine is given at birth, 6 weeks at 10 weeks, and 14 weeks old.
- Hepatitis B - This vaccine protects against the viral Hepatitis B infection of the liver. It is administered at birth, at 6 weeks at 10 weeks old, and at 14 weeks old.
- DTwP / DTaP - Diphtheria combined with tetanus and pertussis (whooping cough disease) vaccines. It is given to the baby at 6, 10 and 14 weeks of age.
- Rotavirus - This vaccine protects the baby against severe diarrhoeal disease and is given when the newborn is 6, 10 and 14 weeks old.
- PCV - This vaccine protects against pneumonia, meningitis, septicemia, sinusitis and otitis media, which is given at 6 and 14 weeks.
- Influenz (IIV)-The Inactivated Influenza Vaccine, which is given at 6 & 7 months of age protects the baby from contracting influenza.
- Typhoid Conjugate Vaccine – This vaccine protects the baby from typhoid disease.
- MMR – The Measles, Mumps, and Rubella is given at 9th and 15th month and protects 3 diseases - measles, mumps, and rubella.
- Hepatitis A – At 12th month Hepatitis A vaccine is given which protects the baby against Hepatitis A, a deadly viral infection which attacks the liver.
History of Vaccination in India
It was in May 1802 that the first vaccine arrived in India. It was issued to treat the smallpox epidemic, and on the 14th of June, 1802, Anna Dusthall, a three-year-old kid from the erstwhile Mumbai, became the first person in India to receive it.
From then till date, paediatric vaccinations have been conducted gradually across the length and breadth of India, delivering wholesomeness and healthy living. The immunisation drive was so much of a roaring success that the World Health Organisation (WHO) had declared the elimination of smallpox and polio from the face of the globe by 1980.
Herd immunity
It is more difficult for an infectious virus to spread in a community when a large number of individuals are immune to it. This is called herd immunity which can be typically achieved through vaccination. Prior to vaccination, natural attainment of herd immunity was only possible with direct infection, which posed a threat of fatality.
Through herd immunity, even the people who are not immune to a disease can be protected, such as those who:
- never contracted the disease
- can't get vaccinated
- cannot become immune because due to a weak immune system
When about 70-80% of people are immune to an infection, the entire community is usually protected.
Financial and evolutionary advantages of vaccines
Baby vaccinations can save families time and money by preventing vaccine-preventable diseases that can result in prolonged disabilities and financial burdens. Vaccinations have also eliminated many diseases that were once common and deadly, protecting future generations from these illnesses.
By continuing to vaccinate now, parents can help ensure that some diseases of today will no longer exist to harm their children or future generations.
Tips on immunisations for babies and children
There are a few tips which the parents need to be aware of to understand vaccinations and their smooth reruns.
- The parent must look out for any swelling at the injection site, pain, and fever, as they are common adverse effects of vaccines. These side effects must be discussed with the doctor and inquired about, which symptoms needed a visit.
- Do not forget to bring your child's vaccination record to all office visits, and ensure that the doctor signs and dates each vaccination.
- Healthcare centres often maintain an immunisation reminder or recall system. Know if the center you have been to have one of those, and if so, do register. This system reminds you not only about the due immunisations but also will warn you in case of any missed immunisation.
Vaccination chart for babies in INDIA | Download 👇