PAP Smear Test after 30 years – Preparation, Procedure & Risk factors

What is pap smear test?
Pap smear test meaning
A pap smear test (also called as Pap test) is used to screen cervical cancer in a woman. The test generally involves the collection and examination of cells from the cervix region (lower and narrow end of the uterus) for the existence of abnormal cells leading to cancer.
Pap smear full form - The Papanicolaou test (Pap test)
Early pap smear screening for cervical cancer improves the likelihood of successful treatment. A cervical pap smear can also detect the presence of precancerous cells (abnormal cells) and is also the first step in preventing cervical cancer.
When should I go for screening?
As per the American College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (ACOG) recommendations, the screening should start at 21 years, irrespective of sexual status.
- Women aged between 21-30 years should have a pap test every other year; if more than 30 and has three normal PAP tests in a row, then the frequency can be changed to every three years.
- Women with weak immune systems, a history of abnormal cervical cells and the presence of high-risk factors for cervical cancer should be having more screening tests.
- Women between the ages of 65 and 70 with three normal pap tests in a row, sexually inactive, and who never had an abnormal pap test may no longer need to be screened for cervical cancer.
- If the woman had a total hysterectomy (removal of the uterus and cervix), there is no need to have a screening test unless she has a history of prior surgery for cervical cancer or pre-cancer.

Why pap smear test is done?
The gynecologist advises having a pap smear to detect the presence of the following conditions in the cervical area:
- Abnormal or precancerous cells
- Cervical inflammations
- Infections
Human papillomavirus (HPV) testing may be performed simultaneously with a pap smear by the gynaecologist. For women over the age of 30, HPV infection is the greatest risk factor for developing cervical cancer.
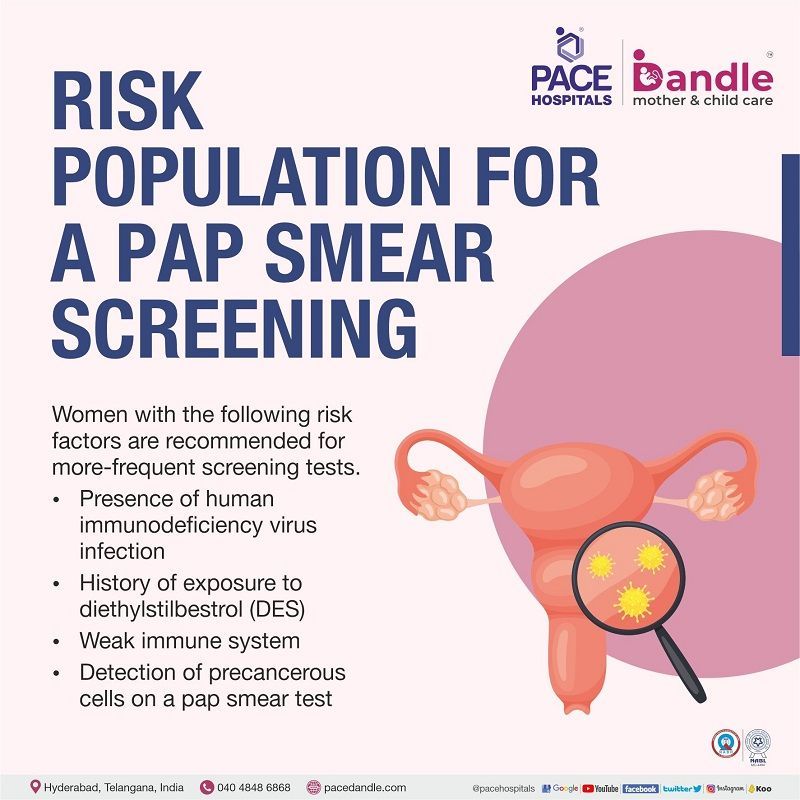
Who all are at risk for a Pap smear screening?
Women with the following risk factors are recommended for more-frequent screening tests.
- Presence of human immunodeficiency virus infection
- History of exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES)
- Weak immune system
- Detection of precancerous cells on a pap smear test
How to prepare for pap smear test?
The gynaecologist will go through the entire pap smear procedure, including the potential risks, and answers any patient questions.
- The gynaecologist would like to know if the patient is sensitive or allergic to medicines, latex, or tape and using medications that include herbals, birth control or hormone therapy, and other over-the-counter pills.
- The gynaecologist would also like to know the patient's last period, pregnancy status and if the patient has a history of bleeding disorders or using any blood-thinning medicines.
- The gynaecologist advises not to use any douche, lubricants, spermicidal foams, jellies, or creams in the vaginal area for at least 2 to 3 days before the test and to abstain from sexual activity for 24 hours prior to the test.
- The gynaecologist would advise emptying the bladder before the procedure starts.
- A sanitary pad may be advised to counter any spotting that may occur after the test.
How is pap smear test done?
Pap smear test procedure steps
The Pap smear test procedure includes the following:
- The patient will be requested to wear a medical gown.
- The patient will have their feet resting in stirrups on an examination table.
- A speculum is a device used by the gynaecologist to get into the vagina. The cervix can then be viewed through the opening created in the vagina by spreading its walls apart.
- The gynaecologist will use a small brush, swab, or spatula to scrape cells smoothly from the cervix and back of the vagina. The collected cells will be placed in a liquid-filled vial or smeared onto a glass microscope slide.
- The gynaecologist will collect sample cells for HPV tests if needed.
- In case of symptoms of vaginal infection, the vaginal cells will be collected.
- The gynaecologist performs a pelvic exam, and the collected cells will be sent for laboratory analysis.
What happens after a Pap test?
After the procedure, the patient needs to take rest before heading home. The patient might have bleeding from the cervix due to scraping.
In addition to bleeding, the patient might have the following
- Increase in body temperature
- Foul smell vaginal discharge
- Severe pain in the abdomen
Pap smear test result
The cervical pap smear test result could take longer than 20 to 21 days to arrive. If the test findings are normal, the woman might have a very low probability of developing cervical cancer. If the test results indicate positive, the patient needs to visit the gynaecologist for further follow-up.
Frequently asked questions